
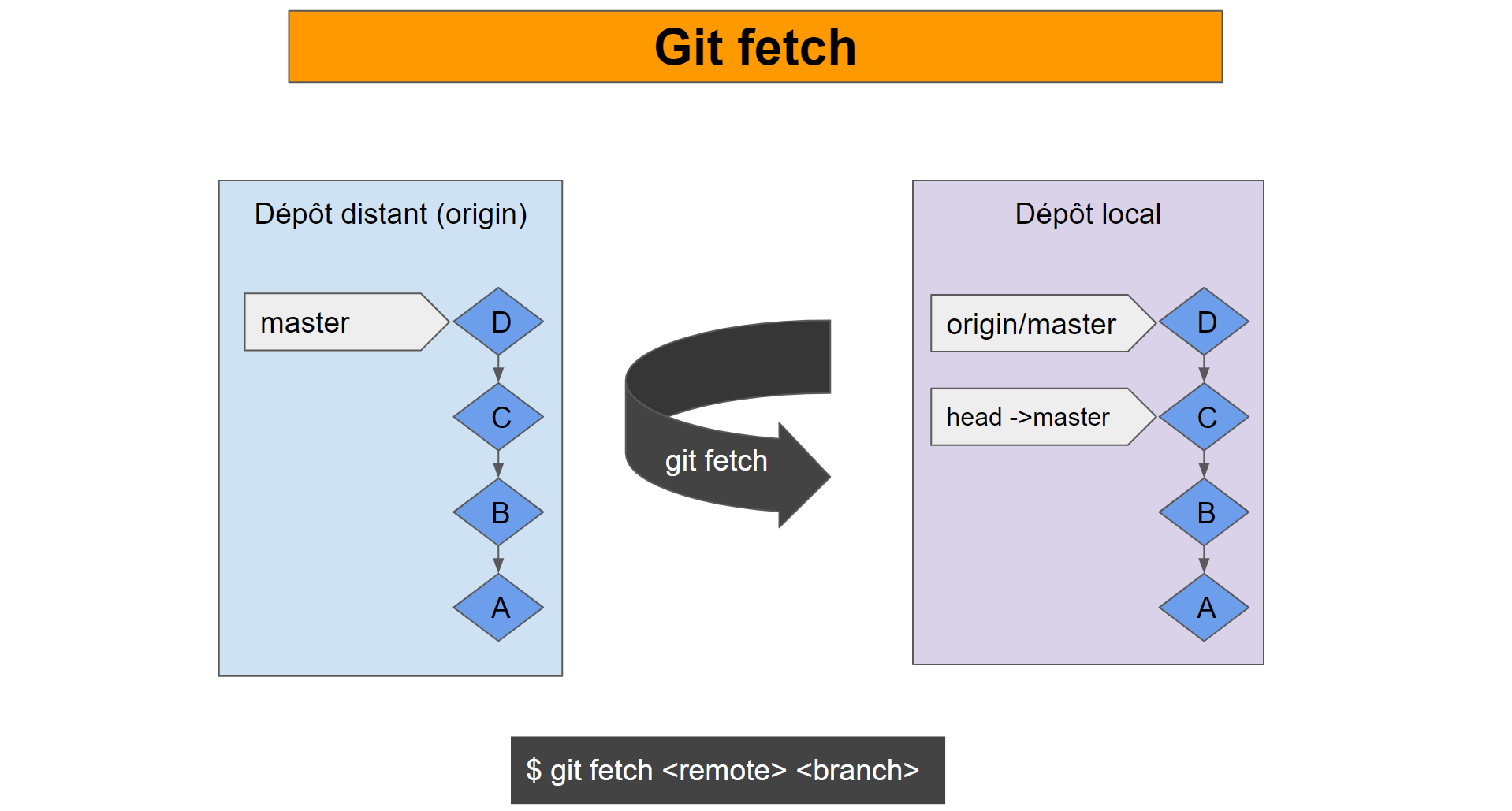
#Git fetch a specific branch update#
For more information, see Update branches with merge or rebase and When to rebase vs. However, Git merge and Git rebase use different strategies. Both Git merge and Git rebase update a target branch by applying commits from a source branch onto it. Or, you can run Git pull, which combines a Git fetch with a Git merge or rebase. If you decide to update your current local branch with fetched changes, you can perform a Git merge or rebase. To remove stale remote-tracking branches, run Git fetch with the -prune flag, or configure Git to prune remote-tracking branches during Git fetch.Īfter a Git fetch, you can compare a local branch with its corresponding remote-tracking branch to see what changed on the remote branch. In the Commit Details window, the changed files are listed in the Changes section.ĭouble-click a changed file to open a diff view of changed content.īy default, Git fetch won't delete remote-tracking branches in your local repo cache that no longer have a remote counterpart. In the Incoming Commits section, right-click a commit and then choose View Commit Details to see the changed files. When downloaded, fetched commits will appear in the Incoming Commits section. In the Synchronization view, choose Fetch. In Team Explorer, select Home and then choose Sync to open the Synchronization view. You can use Git features from either interface interchangeably. To use Team Explorer, uncheck Tools > Options > Preview Features > New Git user experience from the menu bar. Visual Studio 2019 version 16.8 and later versions provides a Git version control experience while maintaining the Team Explorer Git user interface.

Set the Prune remote branches during fetch option to True.Select Tools > Options > Source Control > Git Global Settings.To configure Visual Studio to prune stale remote-tracking branches during a Fetch: This article provides procedures for the following tasks:įetch won't delete remote-tracking branches in your local repo cache that no longer have a remote counterpart. Visual Studio uses a subset of those Git commands when you synchronize your local repo with a remote repo.įor an overview of the Git workflow, see Azure Repos Git tutorial.

Git pull performs a fetch and then a merge or rebase to integrate fetched commits into your current local branch.Git rebase integrates commits from a source branch into a target branch, but uses a different strategy than Git merge.Git merge integrates commits from one or more source branches into a target branch.The remote-tracking branches in local repo cache are updated-local branches remain unchanged. Git fetch downloads any new commits that others uploaded to the remote repo.These Git commands update your local repo: When there are several contributors to a project, keep your local Git repo updated by downloading and integrating work that others uploaded to the project's remote repo. Azure DevOps Services | Azure DevOps Server 2022 - Azure DevOps Server 2019 | TFS 2018


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
